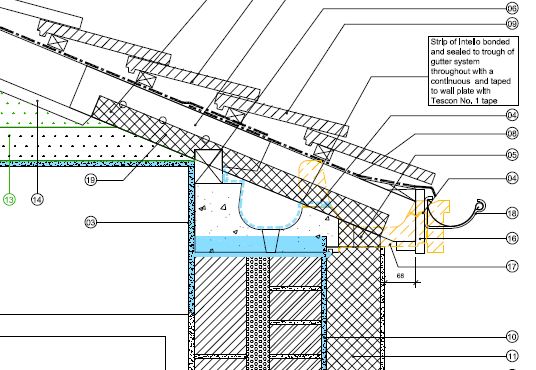
The existing concrete gutters are carefully cut off in line with the external brickwork of the wall using a rotary saw with a clutch which takes a 14 blade.
Concrete gutters condensation.
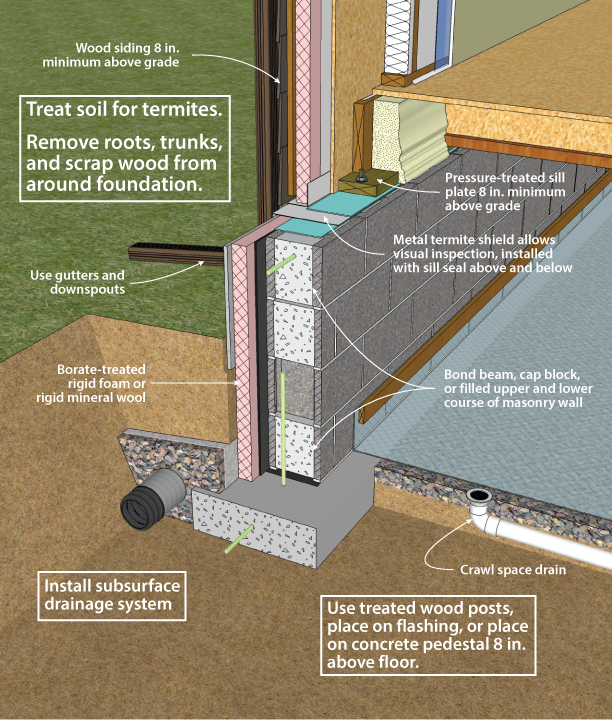
Moisture is generated inside of basements from people and their activities.
When basements are finished these activities increase.
Concrete sweating usually occurs when warm air encounters a colder temperature concrete slab.
If you have concrete in your home that routinely appears to be wet or feels damp then you may have sweating slab syndrome.
Rather than copy existing companies we have based our replacement techniques on scientific principles and calculated engineering resulting in class leading performance that ensures the eradication of the problems associated with concrete gutter systems.
What do finlock gutters look like.
Once the walls of your property were completed the concrete blocks for the guttering were placed on top.
We replace concrete finlock gutters throughout the uk with new maintenance free plastic roofline products.
A 14 blade is the smallest size which will cut completely through the 150mm thick concrete gutter system.
This is not actually a problem with the construction however but an issue that can often be controlled or eliminated by changing the upkeep of the area and in some cases the controlled climate conditions.
Another source that can be thought of as internal is the moisture contained in new concrete after construction.
They are easy to spot once you know what you are looking for.
Concrete gutters are designed in blocks.
Common sources are humidifiers unvented clothes dryers showering and cooking.
Mortar was then used to fix them in position and to fill the small gaps between the blocks.
The concrete gutter is solid from outside to inside and so when it is cold outside the concrete sections are colder inside than the adjacent surfaces and so attract condensation when environmental conditions are right.
Concrete sweating is often mistaken for a water problem since it is common to see a condensation effect on the surface of the slab.